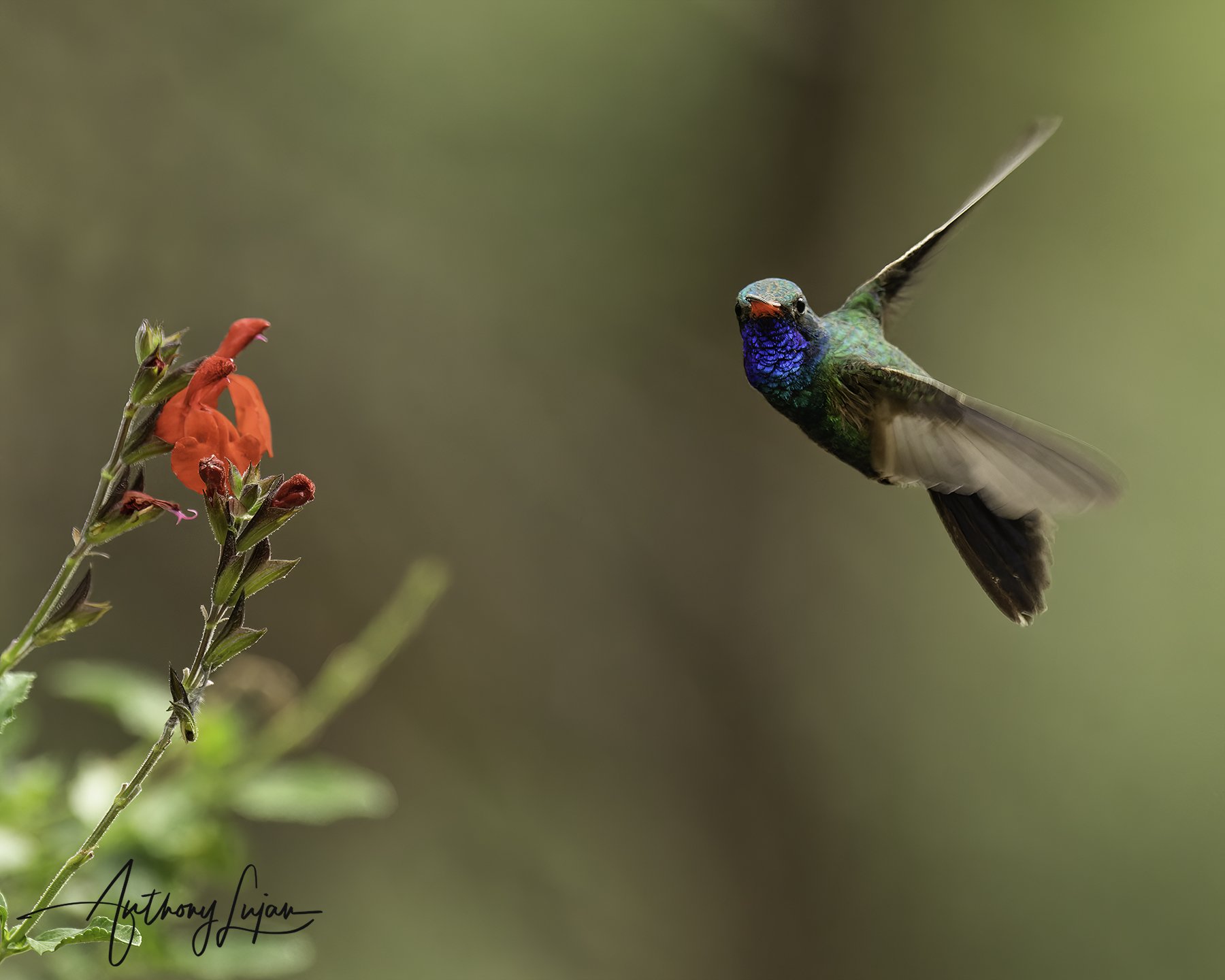How Hummingbirds Stay Safe: Speed, Agility, and More
Hummingbirds, despite their small size, have developed several survival mechanisms to evade predators and stay safe within the food chain:
1. Tiny Nests
Description: Hummingbird nests are very small, carefully hidden, and typically house only two eggs at a time.
Benefit: The small size helps keep nests concealed from predators.
2. Speed
Description: Hummingbirds can fly between 25 to 30 miles per hour.
Benefit: Their speed makes them difficult targets for predators.
3. Diving and Maneuvering
Description: Hummingbirds have the ability to dive at high speeds and maneuver with great agility, similar to a helicopter.
Benefit: This allows them to quickly evade threats and adapt to flight challenges.
4. Wing Flapping
Description: The rapid flapping of their wings produces a humming sound.
Benefit: This sound can confuse predators, making it harder for them to locate the hummingbird.
Conclusion
These adaptations—tiny nests, high speed, agile maneuvering, and wing humming—are crucial for the survival of hummingbirds, helping them evade predators and remain safe in their environment.
Please note: The content provided on this blog is for educational purposes only and contains general information. For advice and guidance tailored to your specific region and circumstances, please consult with a professional.